Synchronous motors are applied on applications that require power factor correction, low starting currents and high torques, and constant speed under load variations with low operating and maintenance costs.

Synchronous motors with brushless excitation system present a rotating exciter, normally located in a compartment in the back of the motor. Depending on the motor operation, the exciter is composed by:
The exciter rotor supplies the necessary power to the motor excitation winding through a rotating, three-phase rectifier bridge.
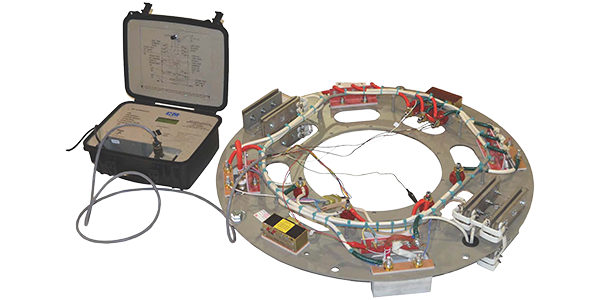
The field application control circuit of the rectification system uses microprocessors to determine the best angle and phase for field application. The Sync-Rite™ system is a high-performance, digitally controlled module developed by WEG Electric Machinery. As an option, a portable Sync-Rite™ testing device can be supplied for easy verification of the circuit electronic components, without the need of disassembling the circuit.
Synchronous motors with static exciter are designed with slip rings and brushes that allow the current supply to reach the rotor poles by means of sliding contact. The direct current must come from an AC/DC static controller and converter located outside the motor. Synchronous motors with static exciter are more often used in applications with variable speed with a frequency drive operation or in applications where the system dynamic response must be extremely fast.
Synchronous motors are manufactured specifically to meet the needs of each application. Due to their construction features, operation with high performance and adaptability to all types of environment, they are virtually used in all industry sectors, such as: Mining, Steel, Paper & cellulose, Sanitation, Oil & Gas, Cement, Rubber, Energy Transmission and others.